
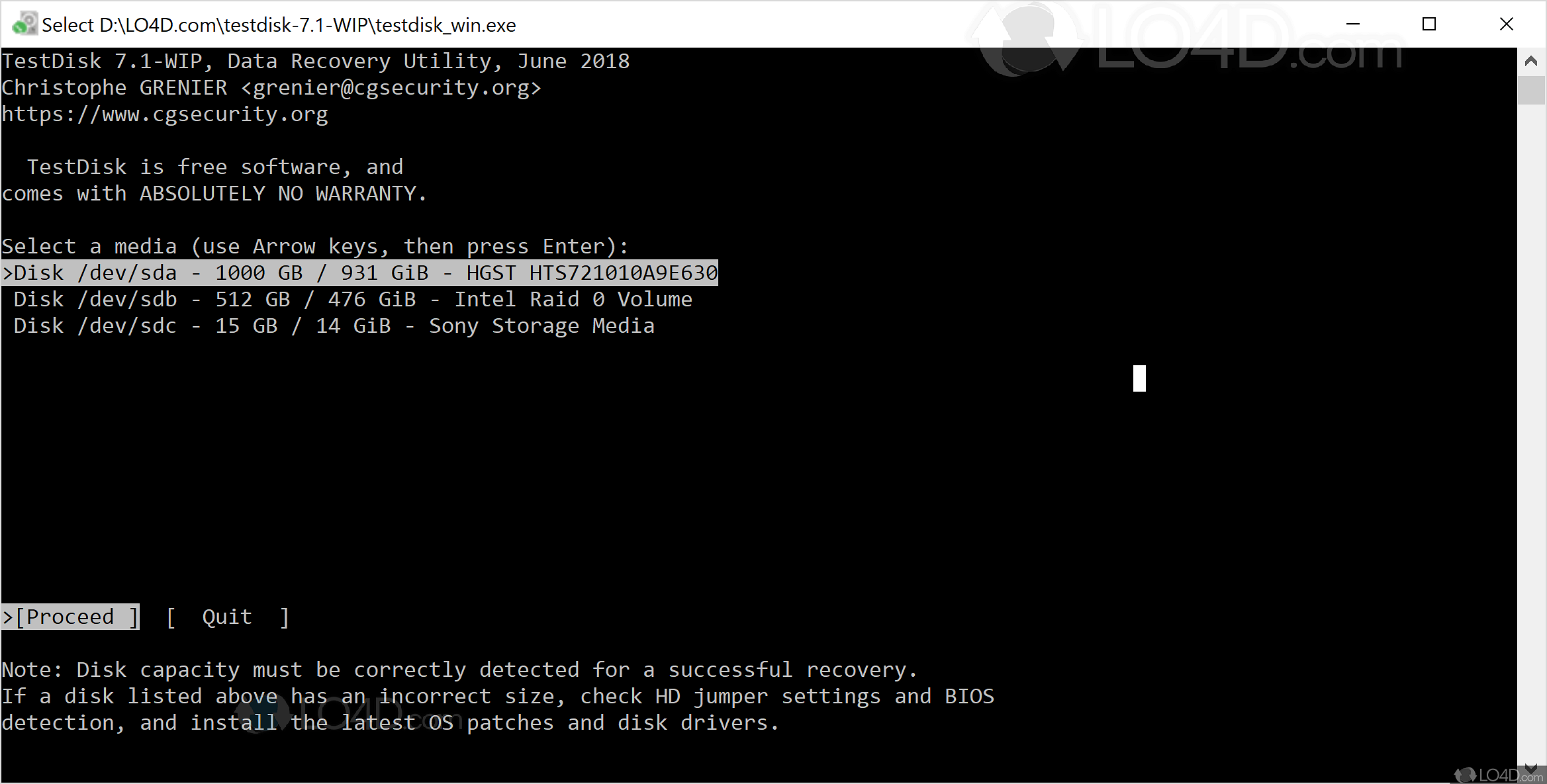

Note: The Testdisk utility tool is beginner-friendly it offers suggestions to the options on each screen.
Testdisk image file how to#
Now proceed further to learn how to recover deleted files in Linux. Great! This confirms that we have successfully installed testdisk. Sample Output TestDisk 7.0, Data Recovery Utility, April 2015Įxt2fs lib: 1.44.1, ntfs lib: libntfs-3g, reiserfs lib: none, ewf lib: none, curses lib: ncurses 6.0 Once you’ve TestDisk installed on your Linux, you can verify the version of testdisk using the command.
Testdisk image file install#
To use testdisk, you must have TestDisk installed on your Linux system using our article: How to Install and Use TestDisk Data Recovery Tool in Linux. In this article, we will show you how to recover deleted files in Linux using the TestDisk data recovery tool. It is useful for recovering data from partitions that are caused by human errors or viruses. The trauma that comes with file and data loss should end thanks to the TestDisk – is a free, open-source software that was initially designed for recovering memory partitions and making non-bootable disks bootable again. I would prefer not to have to restore it as it is just a Windows partition and the only thing I want to recover is some folders from the User and a pst from the default outlook store location.We all know the feeling of looking for a file and not finding it, even in the trash. I have read too that the utility TestDisk should be able to read a disk image. If you use ddrescue to create an image of the hda2 partition, which will be the approximate size of the image? Will it be 400GB or will its size be only the 150GB used space?Īnd once the image is created which is the best tool to see its contents without restoring it? I'm confused about that either as for what I read looks like you should be able to mount it but I tried with a small NTFS partition with no luck.
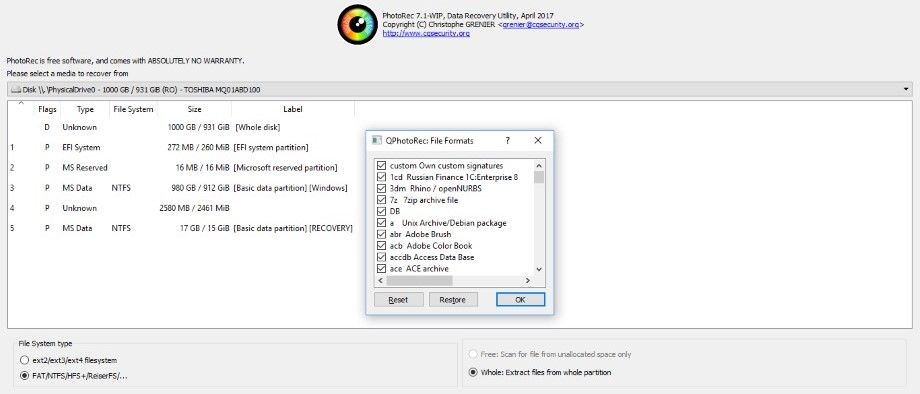
The 400GB partition has 150GB used and 250GB free. So, let's say you have a 500GB disk (hda) with two partitions 100GB (hda1) and 400GB (hda2).
Testdisk image file manual#
And if I understand it correctly you can use ddrescue to create a image file of a drive or a partition too.Īnd what I haven't been able to figure out reading manual is the size of the image. If I understand it ddrescue can be used to clone directly a whole drive to another drive of same or greater size or a partition to other equal or greater same type partition. Chances are the hardware is not damaged but before trying any other thing that could damage the HDD more in case it is damaged I'm going to clone the data. I'm trying to fully understand ddrescue before using it to decide which is the best strategy to recover the most from a maybe damaged HDD.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
